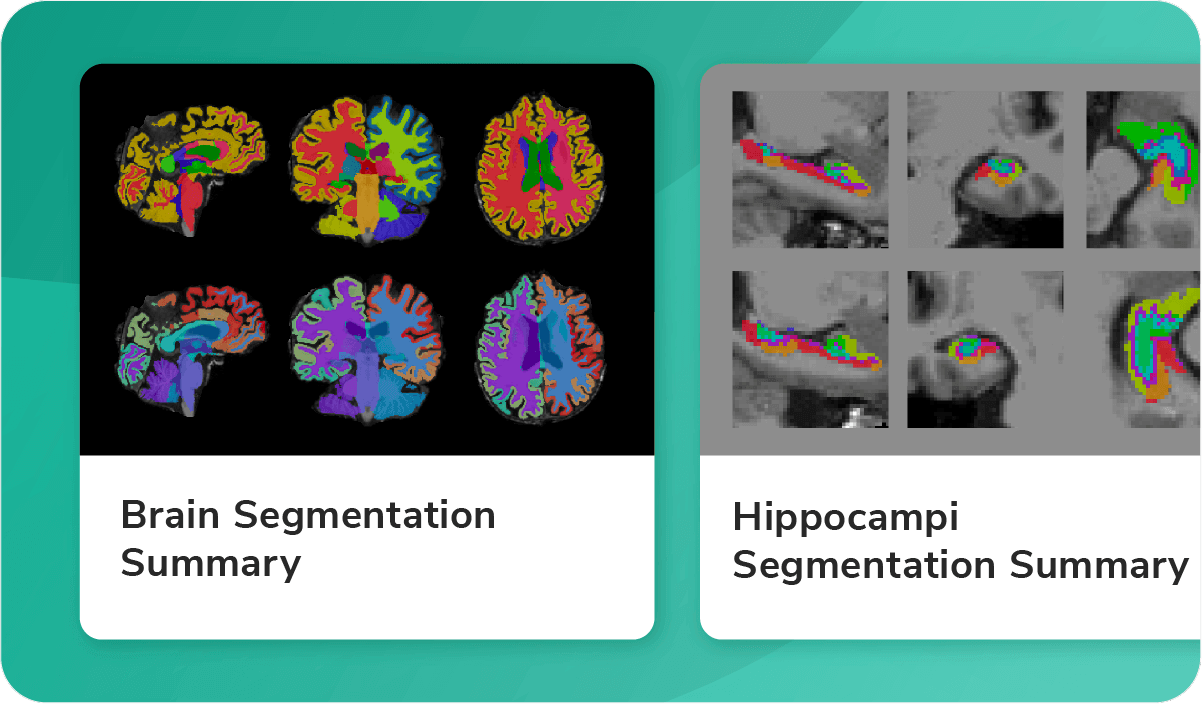
Pioneering Innovations in Medical Imaging for the Central Nervous System (CNS)
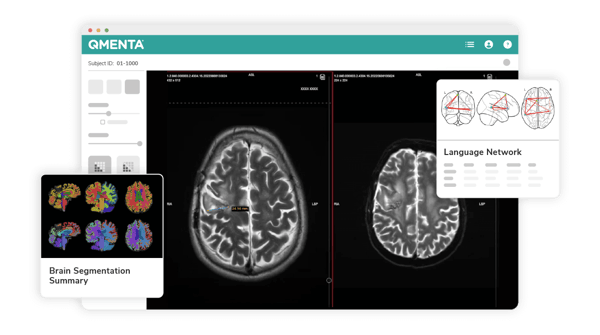
Transforming Neurological Diagnostics and Treatment Through Advanced Imaging Technologies
At QMENTA, we pride ourselves on our extensive expertise in medical imaging within the field of Central Nervous System (CNS) diseases. As leaders in the industry, we leverage the latest advancements in imaging technology to provide detailed insights into the intricate workings of the brain and spinal cord. Our team of highly skilled professionals has a deep understanding of both the clinical and research aspects of CNS imaging. This ensures a comprehensive and nuanced approach to scientific exploration.
We are constantly innovating, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in neuroimaging, and creating transformative tools such as our unique Digital RANO and our advanced QFM (Fiber Mapper) biomarker to quantify major white matter fascicles.
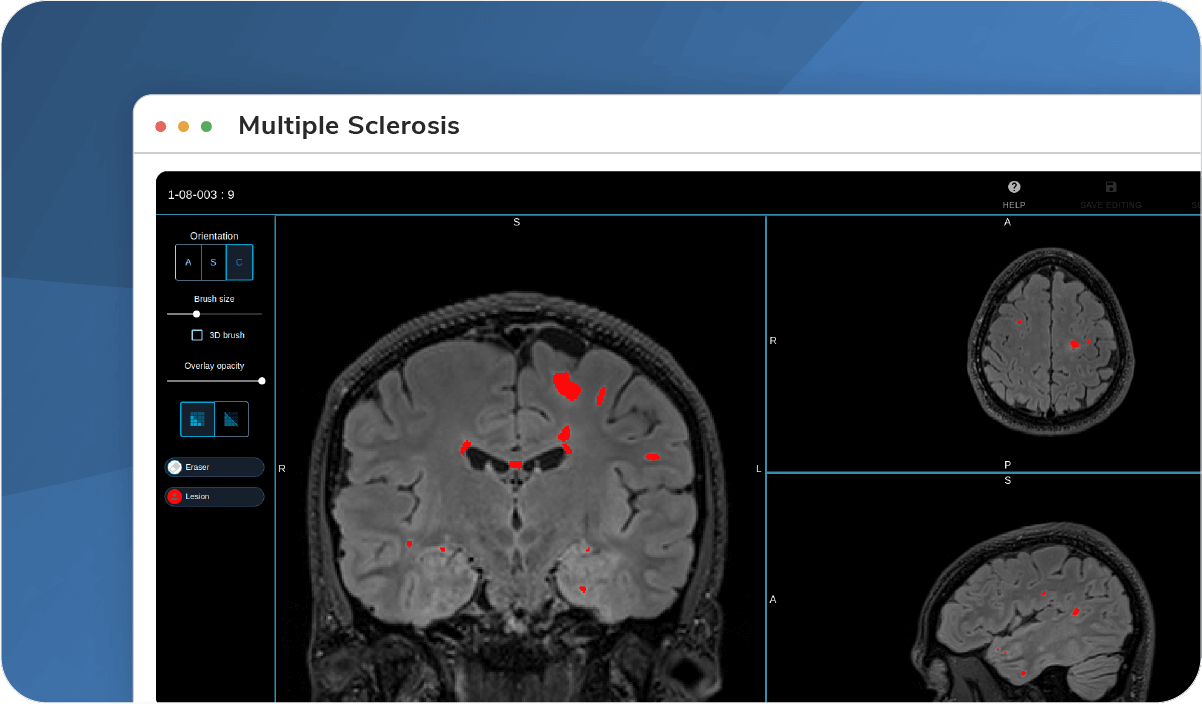
Multiple Sclerosis
State-of-the-art imaging biomarkers and tools for lesion segmentation, activity, load, diffusion, and volume.
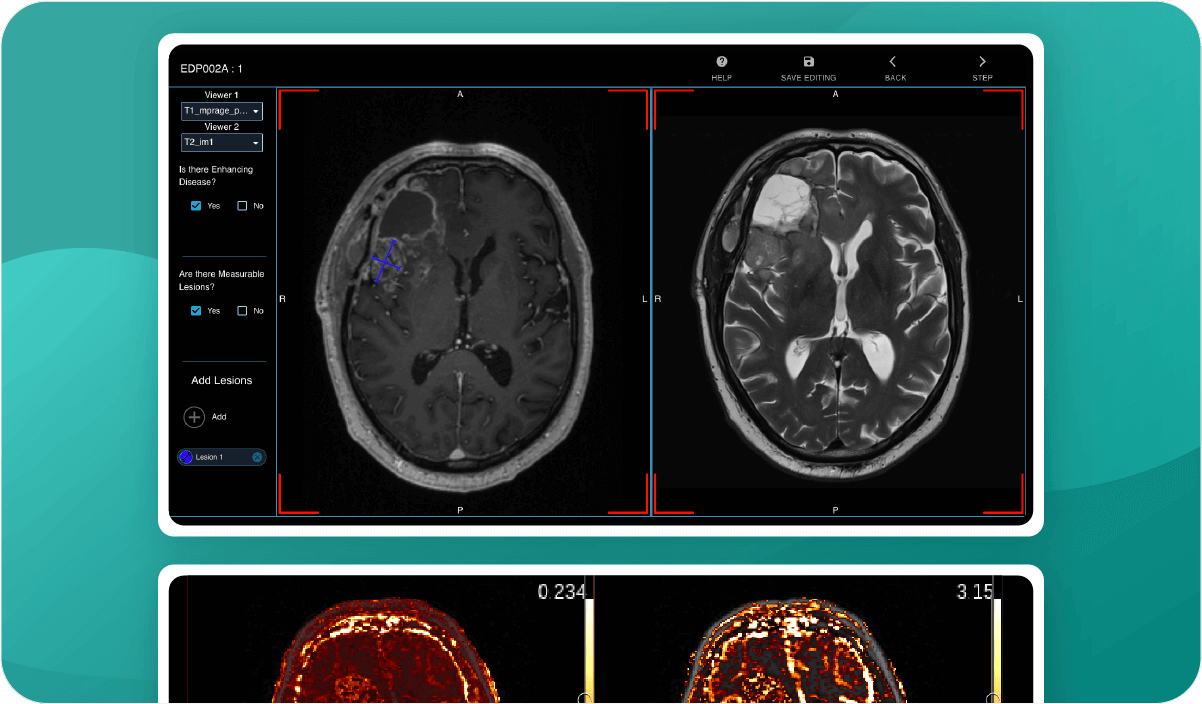
Neuro-Oncology
AI high-tech tools and imaging biomarkers for brain oncology, RANO assessment, contrast, perfusion, tumor volume, and Gadolinium.
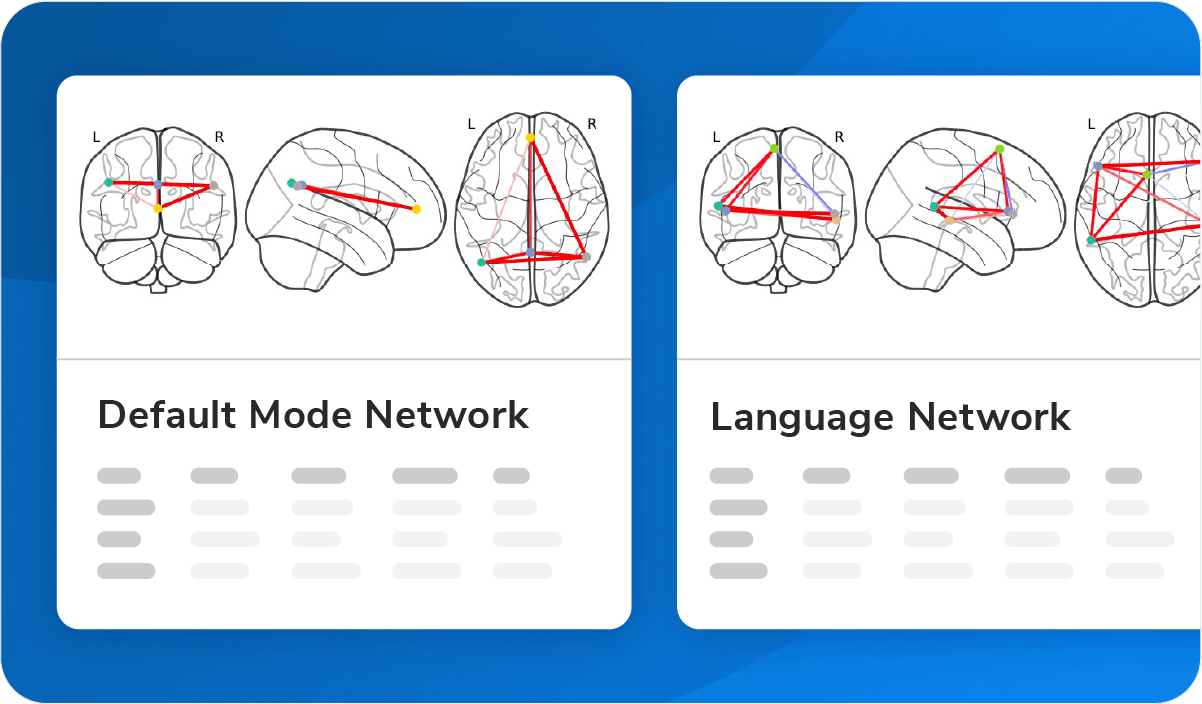
Neuropsychiatric Diseases
Cutting-edge imaging biomarkers for connectivity, volume, and thickness.